A Unified Evaluation Framework for AI Memory Systems


Reliable, Reproducible, and Production-Grade
As long-term memory becomes a core capability for next-generation AI Agents, evaluating memory systems with rigor and fairness has never been more important. To support transparent benchmarking, we built a unified evaluation framework that measures real-world performance of several influential memory systems — including open-source and production-grade APIs.
Evaluation Scope
Beyond EverMemOS, our framework supports four widely used memory systems:
Mem0
MemOS
Zep
MemU
These systems were selected based on their widespread adoption, public benchmarks, and global influence. Because many commercial offerings differ significantly from their open-source versions, we evaluate all systems via their online API endpoints to reflect real production behavior and ensure apples-to-apples comparison.
Implementation Approach
Our adapters are built on:
Official open-source repositories: Mem0, MemOS, Zep
Official documentation: Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep
Unified methodology: identical pipelines, datasets, metrics
Consistent answer generation: all systems use GPT-4.1-mini as the LLM, isolating memory backend performance
During implementation, we identified and fixed several issues in public reference code to ensure each system is evaluated at its best:
Key Adjustments
Mem0 timezone correction
Latest API returns timestamps in PDT; we added timezone normalization for correct temporal reasoning.
MemU retrieval enhancement
The
/related-memory-itemsendpoint retrieves limited context; we followed their documentation to enrich retrieval with category summaries.Zep API migration (v2 → v3)
Public evaluation code still used v2; we fully migrated adapters to the official v3 API.
Zep timestamp semantics
Zep records event timestamps, not conversation timestamps.
Example: “Anna ate a burger yesterday” → stored as March 1 even if discussed on March 2.
Their team provides optimized prompts for temporal questions — we adopted these to ensure fair use of each system as intended.
A core principle emerges: Each memory system uses its own official prompting strategy, rather than force-fitting a unified template.
Evaluation Results
LoCoMo Benchmark
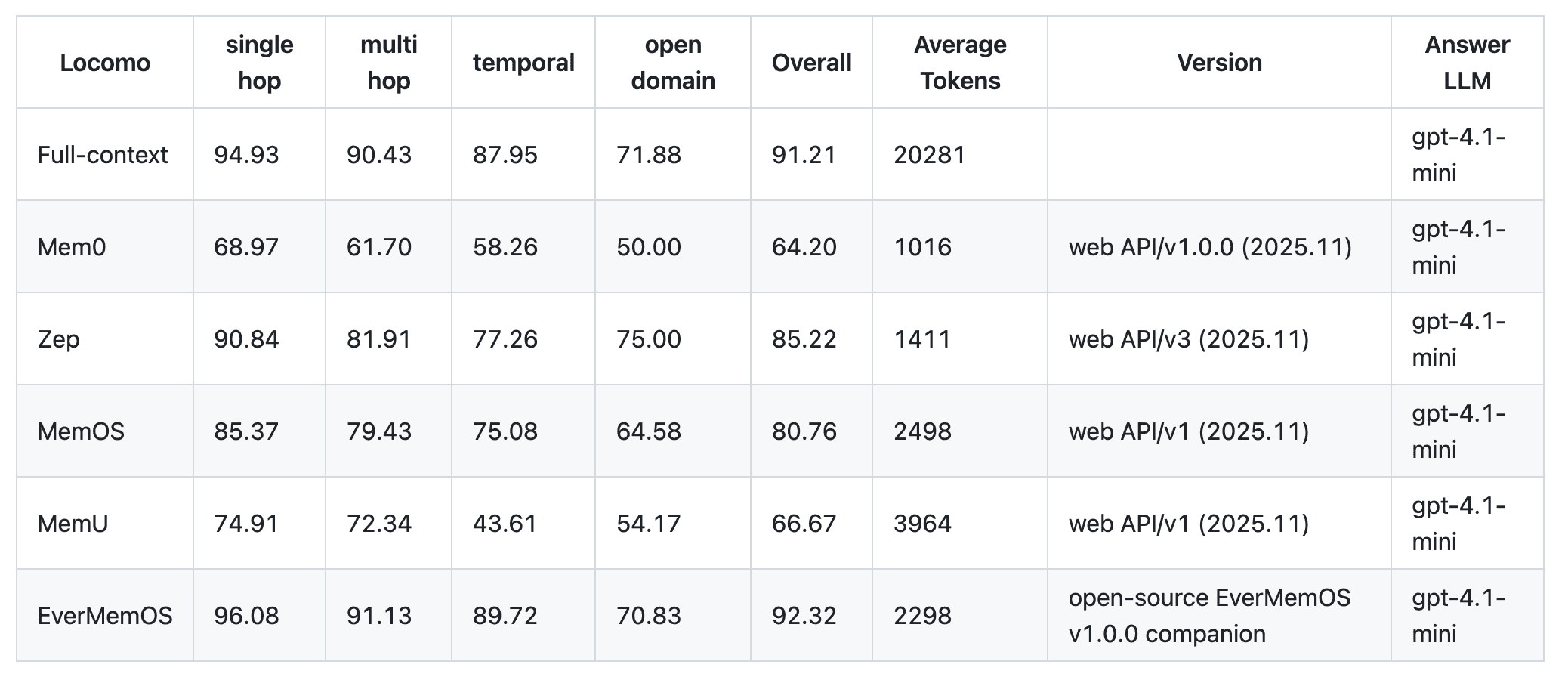
Full-context = baseline that feeds the entire conversation to the model.
LongMemEval
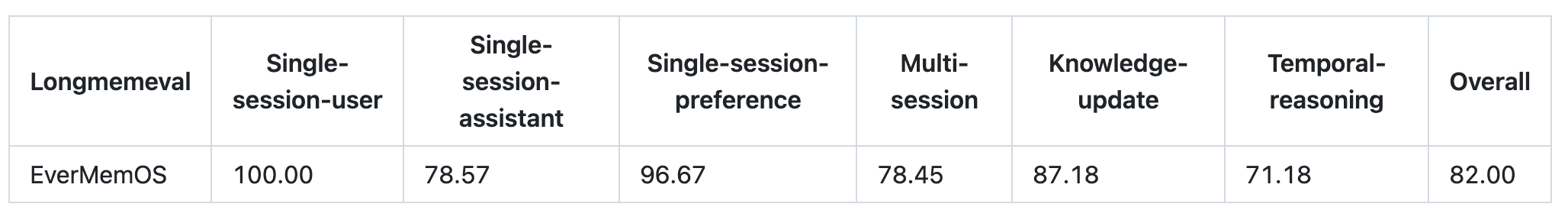
All intermediate data and evaluation outputs are publicly available at EverMind-AI/EverMemOS_Eval_Results for full reproducibility.
Key Framework Features
⭐ Unified & Modular Evaluation Framework
One codebase for all supported systems
Plug-and-play adapters (EverMemOS, Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep)
Multiple benchmarks supported out of the box
Consistent metrics, consistent answer LLM, consistent pipeline
⭐ Automatic Compatibility Detection
The framework automatically adapts to:
Single-user vs multi-user conversation logs
Q&A vs multiple-choice formats
Presence or absence of timestamps
System-specific prompting requirements
⭐ Robust Checkpointing
Resume from any stage: ingestion → search → answer → scoring
Per-conversation checkpoints for search
Per-400-question checkpoints for answering
Closing Thoughts
As long-term memory becomes the foundation of agentic AI, fair and reproducible evaluation is critical. With this framework, researchers and developers can reliably benchmark memory systems across diverse tasks — from temporal reasoning to multi-session continuity — using industry-standard datasets and production-grade APIs.
If you’d like to explore the results or contribute, visit the repository: GitHub
Reliable, Reproducible, and Production-Grade
As long-term memory becomes a core capability for next-generation AI Agents, evaluating memory systems with rigor and fairness has never been more important. To support transparent benchmarking, we built a unified evaluation framework that measures real-world performance of several influential memory systems — including open-source and production-grade APIs.
Evaluation Scope
Beyond EverMemOS, our framework supports four widely used memory systems:
Mem0
MemOS
Zep
MemU
These systems were selected based on their widespread adoption, public benchmarks, and global influence. Because many commercial offerings differ significantly from their open-source versions, we evaluate all systems via their online API endpoints to reflect real production behavior and ensure apples-to-apples comparison.
Implementation Approach
Our adapters are built on:
Official open-source repositories: Mem0, MemOS, Zep
Official documentation: Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep
Unified methodology: identical pipelines, datasets, metrics
Consistent answer generation: all systems use GPT-4.1-mini as the LLM, isolating memory backend performance
During implementation, we identified and fixed several issues in public reference code to ensure each system is evaluated at its best:
Key Adjustments
Mem0 timezone correction
Latest API returns timestamps in PDT; we added timezone normalization for correct temporal reasoning.
MemU retrieval enhancement
The
/related-memory-itemsendpoint retrieves limited context; we followed their documentation to enrich retrieval with category summaries.Zep API migration (v2 → v3)
Public evaluation code still used v2; we fully migrated adapters to the official v3 API.
Zep timestamp semantics
Zep records event timestamps, not conversation timestamps.
Example: “Anna ate a burger yesterday” → stored as March 1 even if discussed on March 2.
Their team provides optimized prompts for temporal questions — we adopted these to ensure fair use of each system as intended.
A core principle emerges: Each memory system uses its own official prompting strategy, rather than force-fitting a unified template.
Evaluation Results
LoCoMo Benchmark

Full-context = baseline that feeds the entire conversation to the model.
LongMemEval

All intermediate data and evaluation outputs are publicly available at EverMind-AI/EverMemOS_Eval_Results for full reproducibility.
Key Framework Features
⭐ Unified & Modular Evaluation Framework
One codebase for all supported systems
Plug-and-play adapters (EverMemOS, Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep)
Multiple benchmarks supported out of the box
Consistent metrics, consistent answer LLM, consistent pipeline
⭐ Automatic Compatibility Detection
The framework automatically adapts to:
Single-user vs multi-user conversation logs
Q&A vs multiple-choice formats
Presence or absence of timestamps
System-specific prompting requirements
⭐ Robust Checkpointing
Resume from any stage: ingestion → search → answer → scoring
Per-conversation checkpoints for search
Per-400-question checkpoints for answering
Closing Thoughts
As long-term memory becomes the foundation of agentic AI, fair and reproducible evaluation is critical. With this framework, researchers and developers can reliably benchmark memory systems across diverse tasks — from temporal reasoning to multi-session continuity — using industry-standard datasets and production-grade APIs.
If you’d like to explore the results or contribute, visit the repository: GitHub
Reliable, Reproducible, and Production-Grade
As long-term memory becomes a core capability for next-generation AI Agents, evaluating memory systems with rigor and fairness has never been more important. To support transparent benchmarking, we built a unified evaluation framework that measures real-world performance of several influential memory systems — including open-source and production-grade APIs.
Evaluation Scope
Beyond EverMemOS, our framework supports four widely used memory systems:
Mem0
MemOS
Zep
MemU
These systems were selected based on their widespread adoption, public benchmarks, and global influence. Because many commercial offerings differ significantly from their open-source versions, we evaluate all systems via their online API endpoints to reflect real production behavior and ensure apples-to-apples comparison.
Implementation Approach
Our adapters are built on:
Official open-source repositories: Mem0, MemOS, Zep
Official documentation: Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep
Unified methodology: identical pipelines, datasets, metrics
Consistent answer generation: all systems use GPT-4.1-mini as the LLM, isolating memory backend performance
During implementation, we identified and fixed several issues in public reference code to ensure each system is evaluated at its best:
Key Adjustments
Mem0 timezone correction
Latest API returns timestamps in PDT; we added timezone normalization for correct temporal reasoning.
MemU retrieval enhancement
The
/related-memory-itemsendpoint retrieves limited context; we followed their documentation to enrich retrieval with category summaries.Zep API migration (v2 → v3)
Public evaluation code still used v2; we fully migrated adapters to the official v3 API.
Zep timestamp semantics
Zep records event timestamps, not conversation timestamps.
Example: “Anna ate a burger yesterday” → stored as March 1 even if discussed on March 2.
Their team provides optimized prompts for temporal questions — we adopted these to ensure fair use of each system as intended.
A core principle emerges: Each memory system uses its own official prompting strategy, rather than force-fitting a unified template.
Evaluation Results
LoCoMo Benchmark

Full-context = baseline that feeds the entire conversation to the model.
LongMemEval

All intermediate data and evaluation outputs are publicly available at EverMind-AI/EverMemOS_Eval_Results for full reproducibility.
Key Framework Features
⭐ Unified & Modular Evaluation Framework
One codebase for all supported systems
Plug-and-play adapters (EverMemOS, Mem0, MemOS, MemU, Zep)
Multiple benchmarks supported out of the box
Consistent metrics, consistent answer LLM, consistent pipeline
⭐ Automatic Compatibility Detection
The framework automatically adapts to:
Single-user vs multi-user conversation logs
Q&A vs multiple-choice formats
Presence or absence of timestamps
System-specific prompting requirements
⭐ Robust Checkpointing
Resume from any stage: ingestion → search → answer → scoring
Per-conversation checkpoints for search
Per-400-question checkpoints for answering
Closing Thoughts
As long-term memory becomes the foundation of agentic AI, fair and reproducible evaluation is critical. With this framework, researchers and developers can reliably benchmark memory systems across diverse tasks — from temporal reasoning to multi-session continuity — using industry-standard datasets and production-grade APIs.
If you’d like to explore the results or contribute, visit the repository: GitHub

